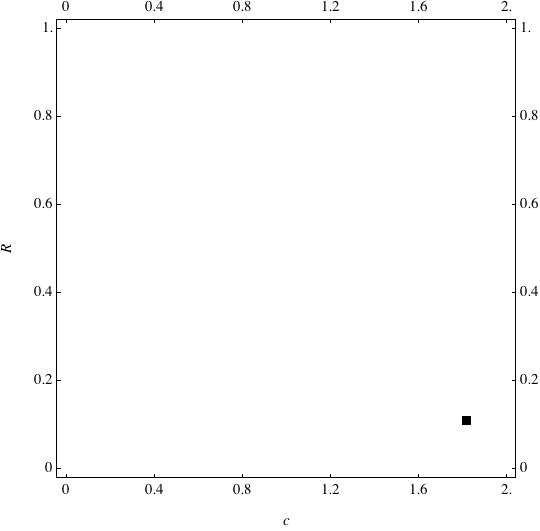
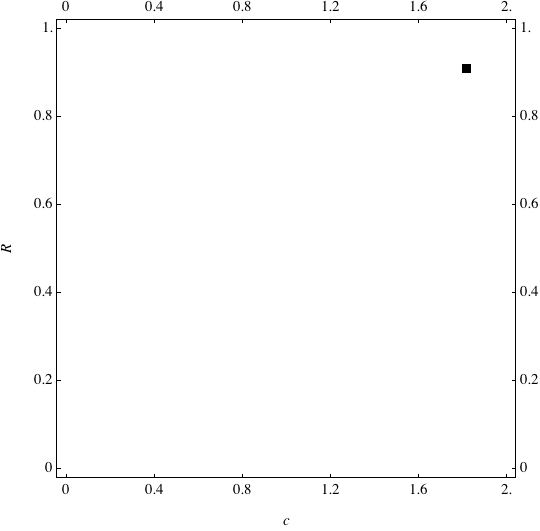
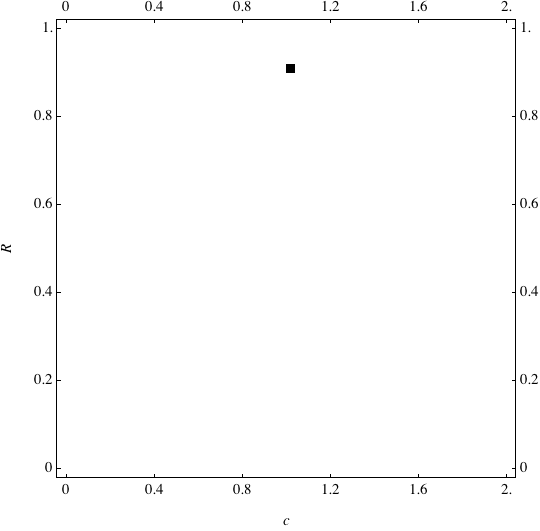
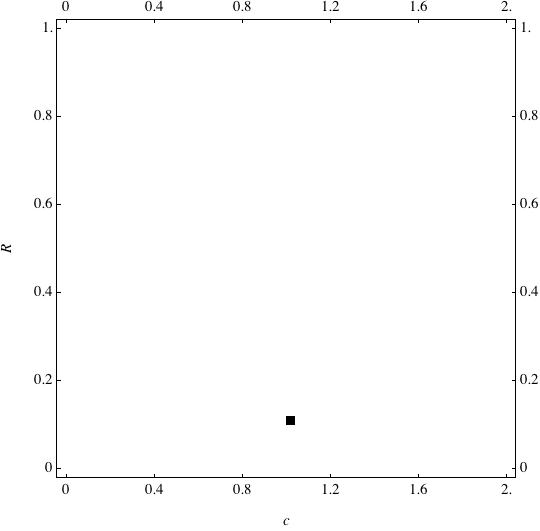
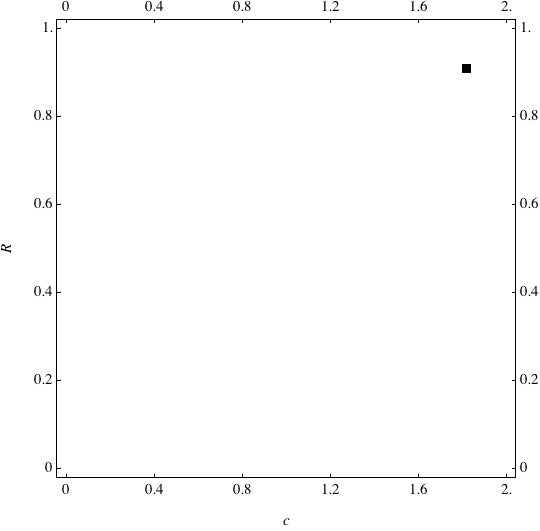
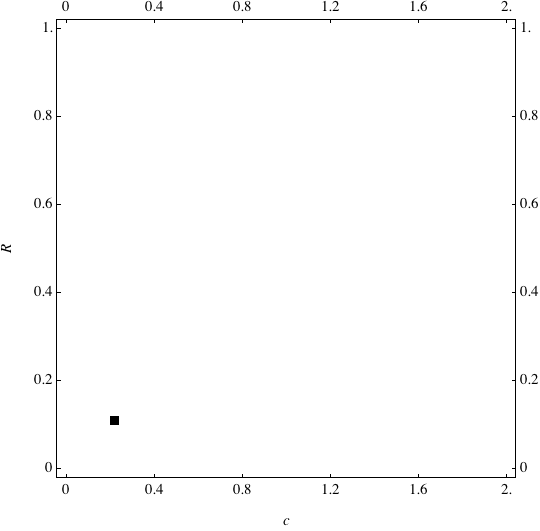
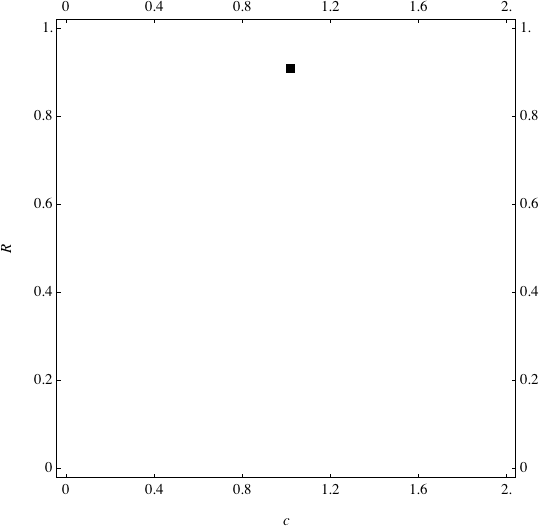
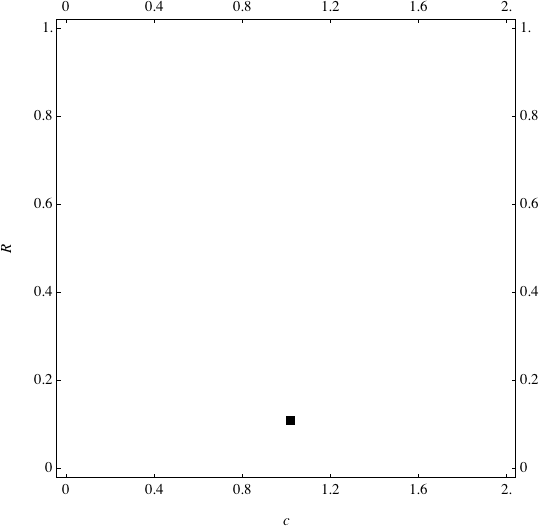
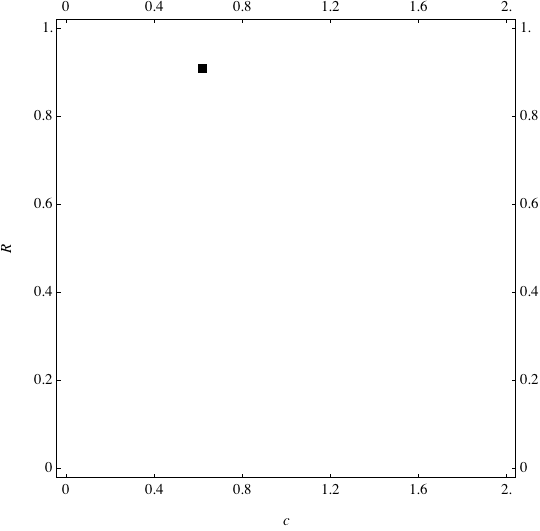
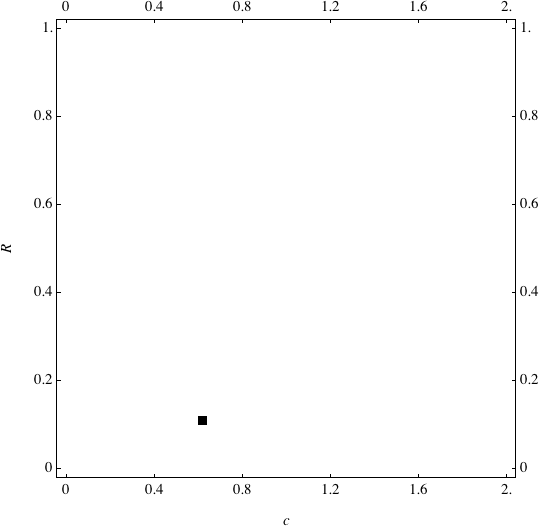
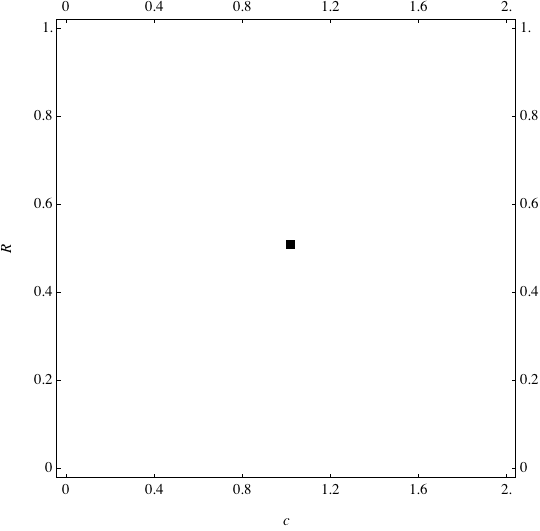
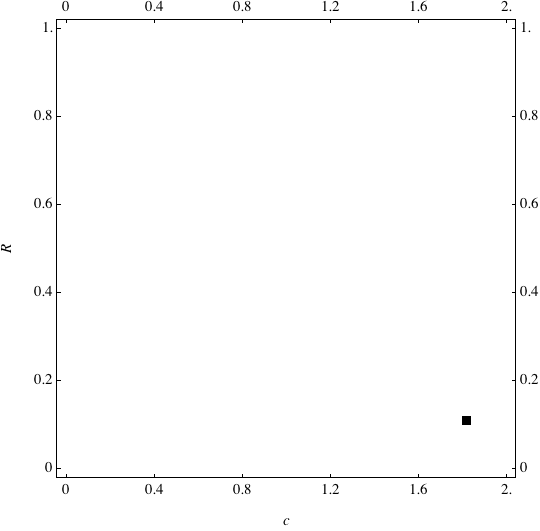
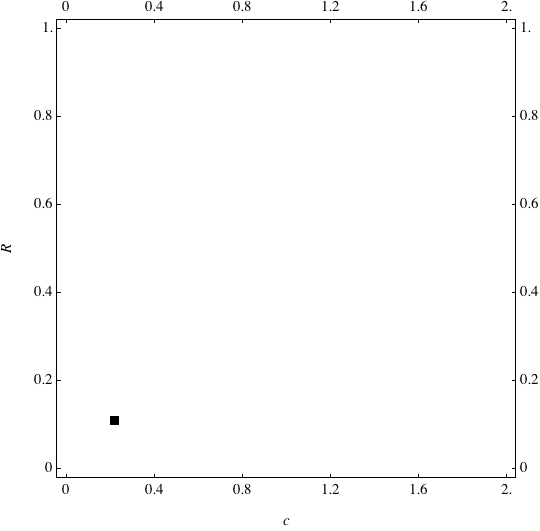
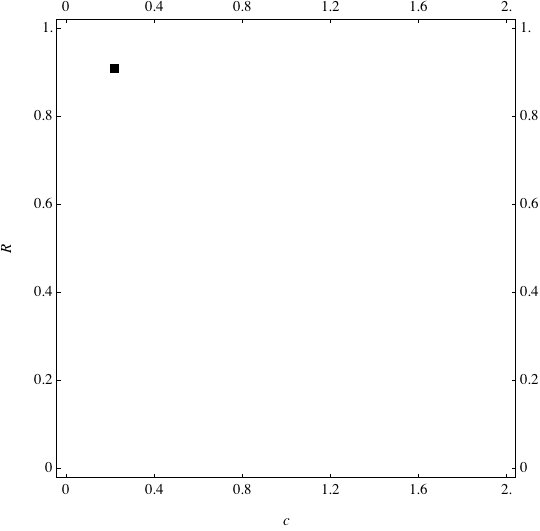
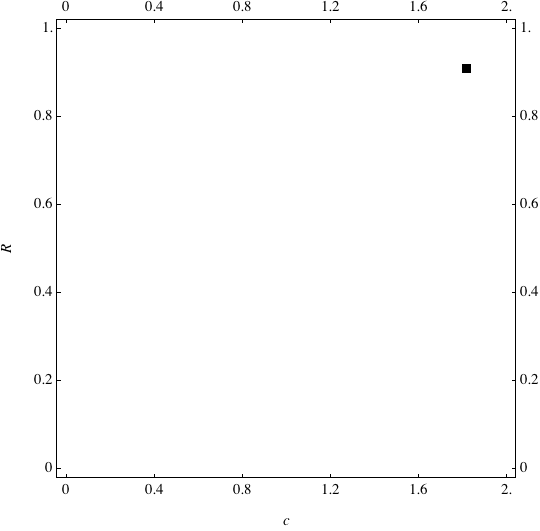
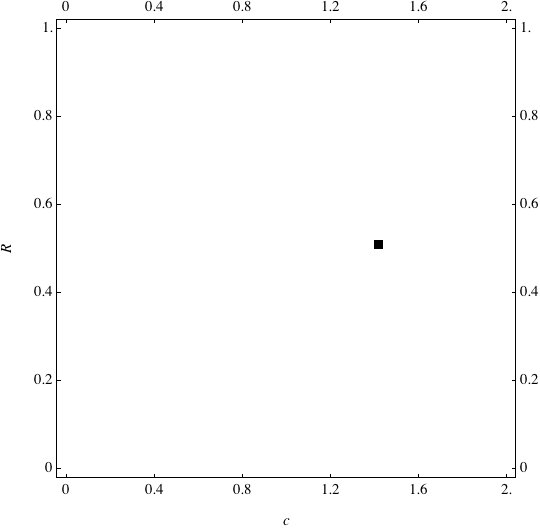
Examples of Coevolution
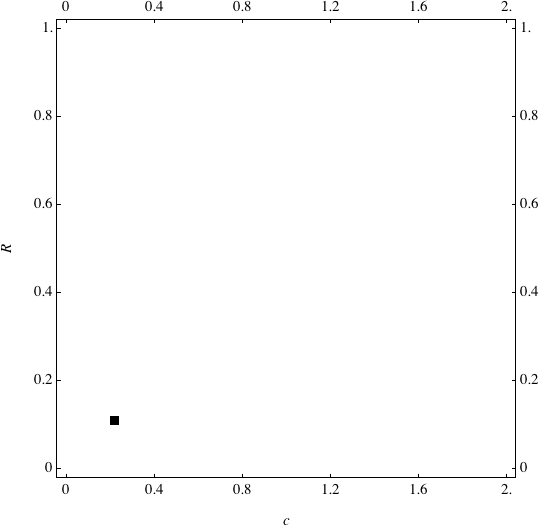
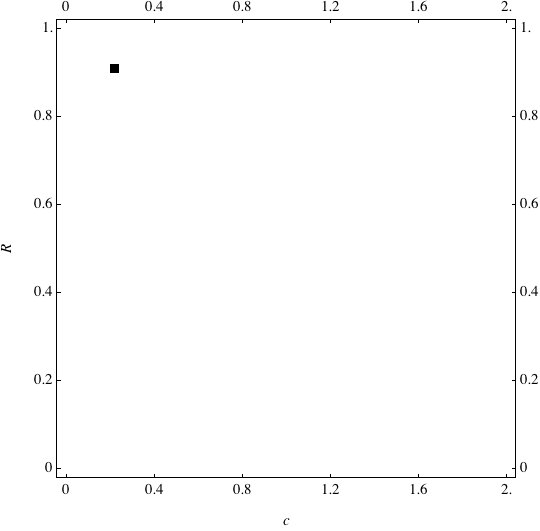
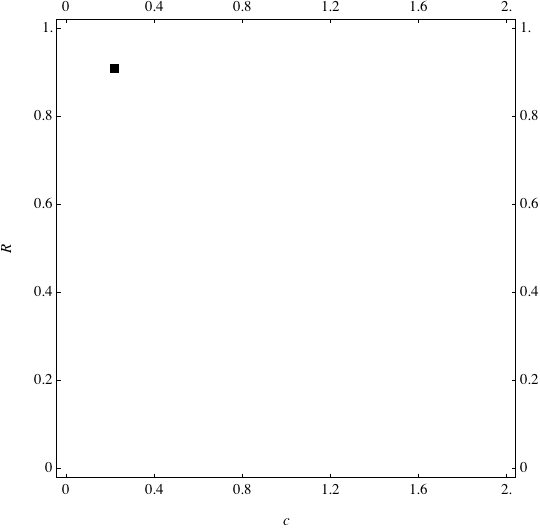
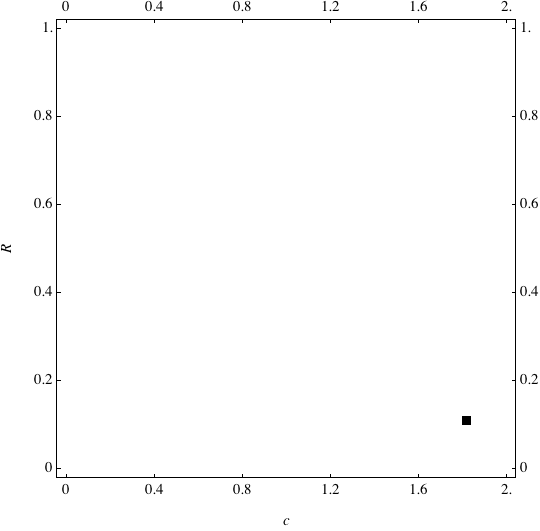
These are examples of evolutionary trajectories of the coevolution of the probability of global reproduction (R: vertical axis, 0 <= R <=1) and the level of cannibalism (c: horizontal axis, 0<=c <= 2).
The trade-off between global reproduction and death rate of juveniles are assumed. Global reproduction is costly and offsprings of disperser have larger death rate, which can be described by,
[death rate of juveniles] = [backgroud death rate] + k*sqrt(R)
where k is a constant for cost. Larger k means more constly (juveniles die more).
Coevolution of the level of cannibalism (c) and the probability of global reproduction (R). Darker means more number of adults (number of juveniles are not shown).Upper panels show initial conditions. Animation will start by clicking the link to gif animations.
k=1.8
k=2.0 (the parameter we used in our paper)
k=2.5